Responsible for the facility:
Grigory M. Arzumanyan
e-mail: This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
Tel. +7 (496) 216-50-69
Kahramon Z. Mamatkulov
e-mail: This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
Tel. +7 (496) 216-49-53
Main research areas:
- Spectroscopy and microscopy of spontaneous and stimulated Raman scattering of light.
- Highly contrast nonlinear
- Single molecule
- Raman spectroscopy of low-dimensinal materials.
- Direct photo- and upconversion luminescence.
- Working with living cells.
- Lipid-protein interactions.
- Spectroscopy of programmed cell death
- Raman markers in biomedicine.
Facility:
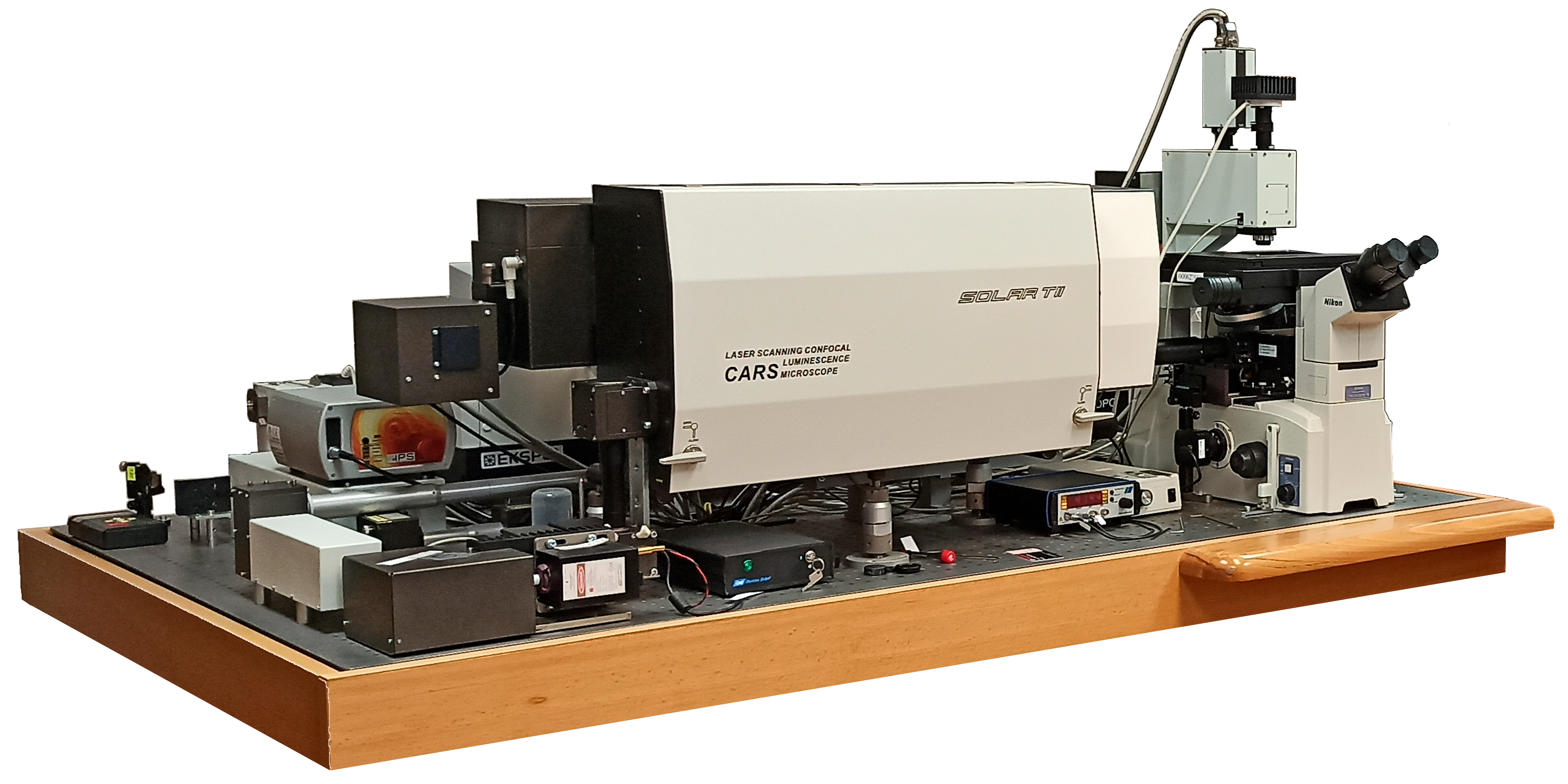
The basic facility for research carried out in the Sector of Raman Spectroscopy (Center "Nanobiophotonics") is a multimodal optical platform based on a 3D scanning laser confocal "CARS" microspectrometer, which enables spectroscopy and microscopy of various materials (solids, liquids, powders, biological samples, etc.) based on spontaneous Raman scattering (RS) of light, surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS), as well as stimulated coherent amplification of light scattering.
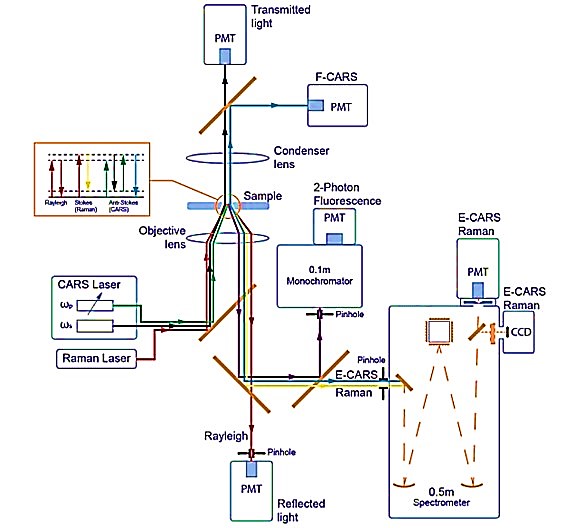
Overview of the CARS microspectrometer
Facility layout
The discovery of laser sources of radiation in the early 1960s stimulated greatly research on nonlinear optical and resonance methods for analyzing matters. For the excitation of nonlinear signals, high-intensity picosecond or femtosecond lasers are used that can simultaneously initiate several nonlinear optical phenomena: harmonic generation (SHG, THG), multiphoton and up-conversion luminescence, coherent anti-Stokes light scattering (CARS), and others.
CARS is a third-order nonlinear optical process involving interactions between pump beam with a frequency ωp, a Stokes beam with a frequency ωs, and the resulting CARS signal at an anti-Stokes frequency ωaS = 2ωp – ωs, generated in the phase matching direction. Vibrational contrast in the CARS process is produced when the frequency difference Δω=ωp-ωS between the pump and the Stokes beam is tuned to resonance with the vibrational mode of the selected chemical bond. In this case, resonant oscillations are coherently generated using excitation fields, thereby creating an intense and directional anti-Stokes signal compared to a weak spontaneous Raman signal (most molecules possess a small Raman cross section ~ 10-30 to 10-25 cm2). CARS signals are 3-4 orders of magnitude more intense than those of the spontaneous Raman scattering process and allow to obtain chemically selective high-contrast images.
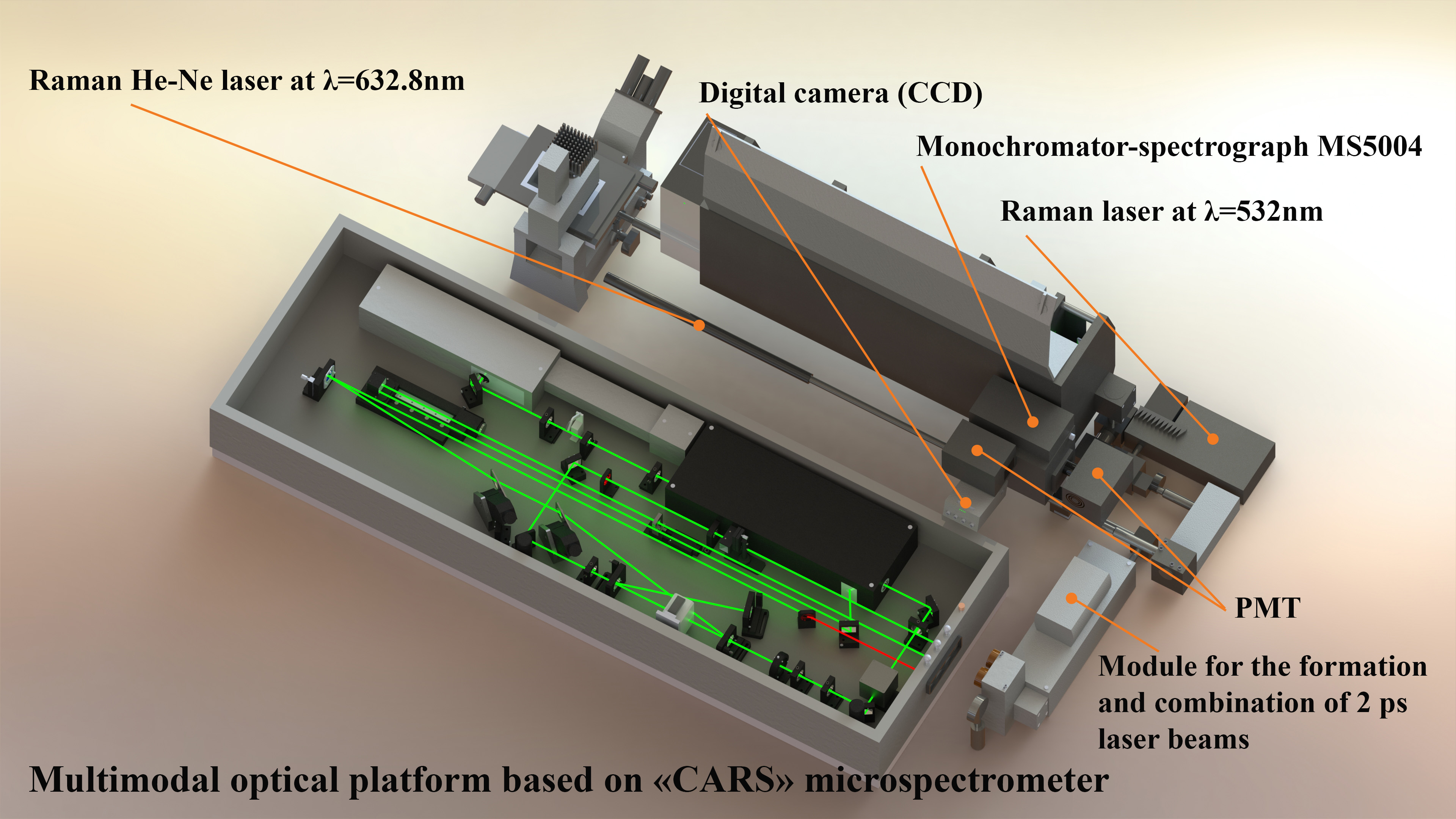
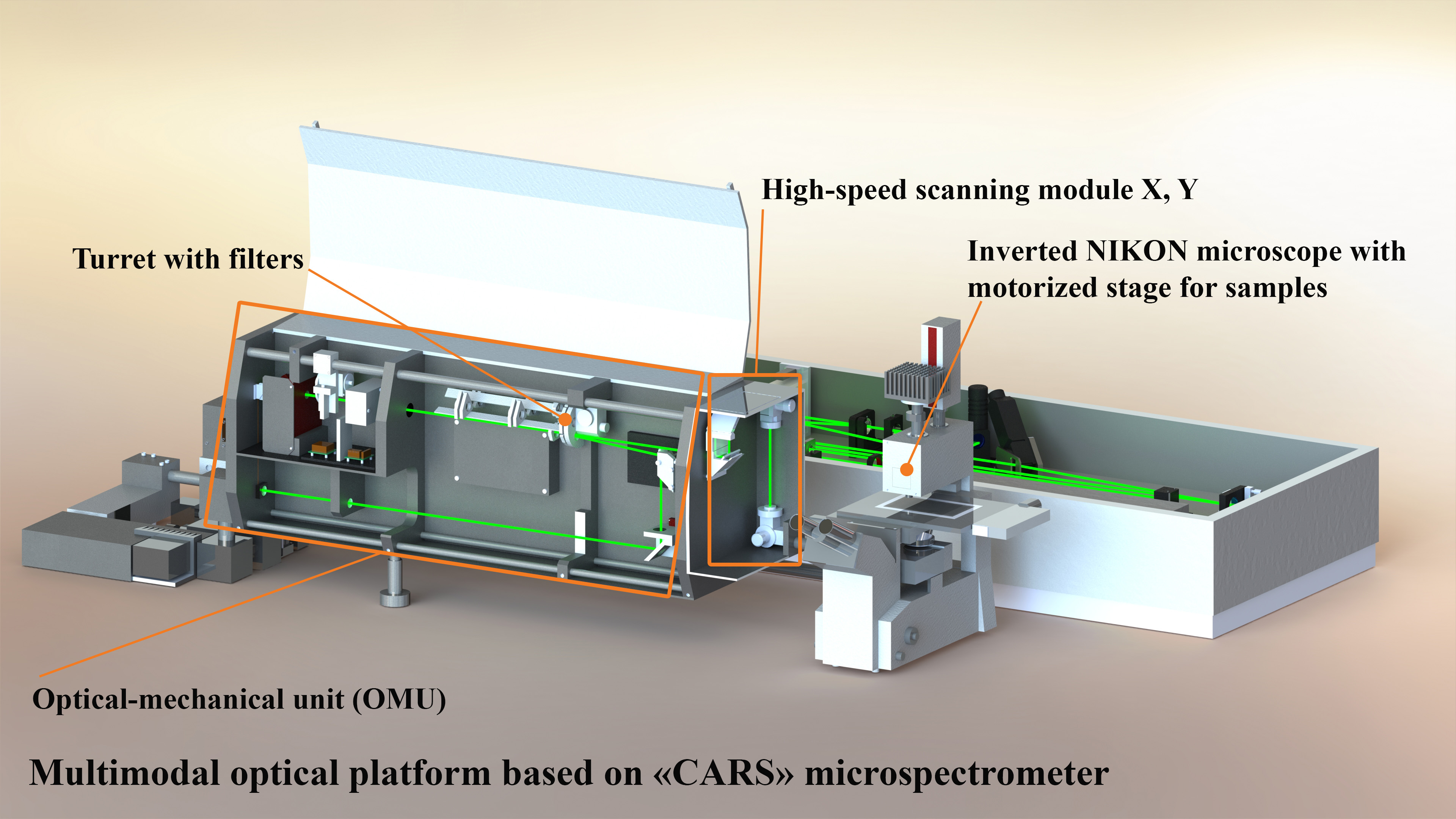
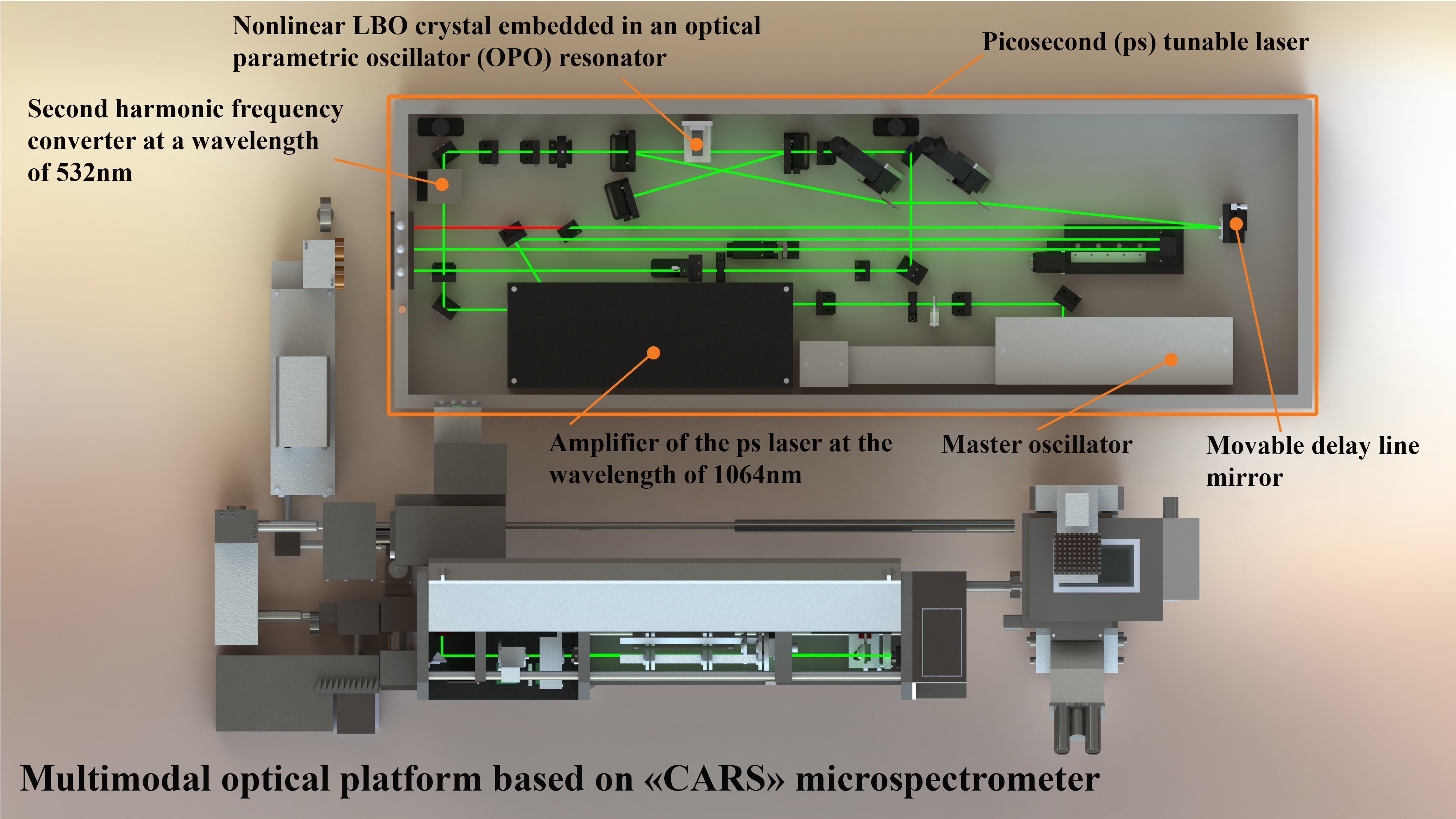
Optical schematic of the basic components and architecture of the CARS microspectrometer
To generate CARS signals, a picosecond Nd:YVO4 laser (Ekspla, PT257-SOPO, Lithuania) tunable in wavelength (690–990) nm with a pulse duration of 6 ps and a pulse repetition rate of 85 MHz was installed on the optical platform of the confocal laser microscope. This laser serves as a source of both a Stokes wave and, simultaneously, a wavelength-tunable pump generated by an intracavity optical parametric oscillator (OPO) with a maximum power of 200 mW and a line width of ~6 cm-1. Depending on the analyzed sample, three lasers are used to generate a spontaneous Raman signal: a He-Ne laser (633 nm) and two diode-pumped lasers at wavelengths of 532 nm and 785 nm.
In order to achieve ultra-high sensitivity in the detection of Raman spectra from low concentrated analyte molecules, down to the single molecule level, various SERS-active substrates, both commercial and those developed at BGUIR, Minsk, Belarus, are used.
The main characteristics of the “CARS” microspectrometer Basic functional modalities Spontaneous Raman, F-CARS, E-CARS, P-CARS, SERS, SECARS, up-conversion luminescence Lasers for spontaneous Raman 532nm (20mW), 633nm (15mW), 785nm (100mW) CARS laser system Picosecond laser Nd:YVO4, Ekspla, PT257 + SOPO Stokes wave: 1064 nm, 6 ps, 5 W Pulse repetition rate: 85 MHz Tunable pump wave: 690 - 990 nm, 150-300 mW. Mode composition: TEM00 Polarization: horizontal Detection system Four channels for high-speed measurements (PMT) and a channel with a CCD camera Spectral registration range Spontaneous Raman: 50 – 6000 сm-1 CARS signal: 990 – 5000 сm-1 Spectral resolution Raman signal: 0.9 сm-1 (grating 1200 gr/mm) CARS signal: 7-8 сm-1 Spatial resolution Microlens 60x with NA-1.2, water-immersion Raman signal: XY < 300 nm, Z ~ 700 nm CARS signal: XYZ < 700 nm Speed scan range With a 60х lens: XY: 225 х 225 µm Spectral measurements and imaging Imaging monochromator-spectrograph MS5004i Digital CCD camera, Proscan, HS 101H Control and automation Full automation
Z: 80 µm
*Testing mode